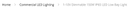1) Link to your most important category and product pages in the sitewide menu
Linking to your key product or category pages from the site-wide menu helps increase the internal authority of these pages. It also gives Google a clearer idea of the sites and hierarchy. Technically speaking, if a page is linked to from the sitewide menu, it means that it is linked to from every page on the site, a clear signal to Google that this page is important.
While this is great for SEO, do take caution as to not overstuff your menu. It’s best practice to keep 5-7 dropdowns in your menu – studies indicate this is the default amount the human short-term memory can hold.
Your menu should ideally only include your top category and product pages, and the rest can be accessed through a ‘view more’ section or linked to from pages already in the menu.
2) Implement breadcrumbs onto your category and product pages
Breadcrumbs are the links at the top of a product or category page which map the user journey to a page (see example below).
Long breadcrumbs are not only useful for user navigation, but they give Google a clear indication of the relationship between a set of category, subcategory and product pages.
These links are a great quick win for eCommerce SEO and also very easy for Google to crawl quickly.
Breadcrumbs should ideally be in the following long format rather than Home > product page as they give Google more context:
-
- Home > Category > Product
- Home > Category > Subcategory > Product
To find out how these can be implemented easily across various e-commerce CMS platforms including Magento and Shopify, we’d recommend reading through the following blog posts:
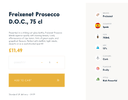
Once breadcrumbs have been implemented, they can be marked up with breadcrumb schema which will appear on the search results. This will give Google further information on the site structure and hierarchy (see SERP example below).
Details on how to implement breadcrumb schema can be found here.
3) Add subcategory links to category pages
Subcategory links give Google more context on the contents of a page, while also allowing web crawlers and users to navigate through the site easily.
These can be implemented as text links at the top of a category page, as shown on the Oliver Bonas site blow:
Or, as image links like the made.com example below:
4) Consider attribute links on product pages
If breadcrumb linking is not currently possible, then attribute linking is a great alternative. Attribute linking is commonly referred to as ‘deep links’ and can work well alongside breadcrumbs if they already exist on the site.
These links can be incorporated anywhere on a product page and reference any attribute a product may have.
One of the main differences between breadcrumb and attribute links is that they do not need to follow a user journey, they can simply include a reference to any category page a product may belong to, e.g. sale and bestseller pages.
You can see an example of how The Bottle Club use these below (sidebar)
You can also see an example below where SKY NEWS uses these as ‘tags’ on blogs to link to relevant hub pages on the site.
5) Make sure your links are crawlable
Make sure to check your links are crawlable internal links! Ensure they are included as <a href> links rather than JavaScript or AJAX, as this will mean Google won’t be able to crawl and follow them, making them redundant.
6) Incorporate a ‘customers also bought/customers also liked’ section
You can easily boost the user experience with internal links like ‘you may also like’ and ‘customers also bought’ modules on a product page. These are very popular on e-commerce sites like ASOS and Patch Plants (see examples below).
From ASOS
From Patch
7) Link from your blog posts to product pages and vice versa
If you have relevant guides or blog posts on the site, these are a great way to link to individual product pages and category pages which perhaps aren’t included in the statewide menu. Even if they are, it’s always best practice to exercise this where possible.
An additional tactic is to see which of your blogs have lots of links to them and add links to pages you want to push (hopefully relevant too). These internal links carry more authority because of the external links to the pages so can be a good tactic.
8) Relevant anchor text
A quick tip for internal linking is to ensure anchor text is relevant. This will give Google more context about the linked-to pages. So instead of “view more” generics, use proper anchor text like “shop accent chairs.”