Intro to Salesforce Commerce Cloud
Salesforce Commerce Cloud gets over half a billion monthly shopper visits from across the globe!
Salesforce Commerce Cloud (SFCC), formerly known as Demandware, is the platform of choice for some of the largest players in the fashion space. Brands that have opted to use SFCC include Marks & Spencer (M&S), Lacoste, and Uniqlo to name a few.
But the platform is not used exclusively by enterprise-level brands. It is becoming increasingly popular among mid-tier retailers who are looking for a better e-commerce solution as it offers greater flexibility around administration and site management.
Why choose Salesforce over other CMS platforms?
From a purely SEO standpoint, Salesforce Commerce Cloud sets itself apart from other CMS platforms with its easily customised functions unrivalled by the likes of Magento or Shopify. Both of which are fantastic, out-of-the-box options but can come with limitations that Salesforce doesn’t.
SFCC can save time and money for smaller businesses When configured correctly, Salesforce boasts short lead times, which are key for any eCommerce retailer. But the real beauty is that this platform doesn’t need to be maintained by development resources – something that often comes with a very high price tag for smaller businesses without in-house development teams.
Salesforce can help to accelerate SEO – not just drive it
Strong SEO strategies have always been key for eCommerce brands but it is fair to say that the presence of COVID-19 has accelerated this need (and then some)!
More and more brick and mortar retailers are investing greater volumes of their marketing budgets into their organic search strategies, and so, in order to be competitive, brands need to be able to pivot and react to consumer demand quickly. This is what SFCC allows you to do and we will now discuss what you need to consider for this to happen.
For the sake of simplicity, here is an overview of the key functions often used by SEO Experts in SFCC – our ultimate guide to Salesforce Commerce Cloud SEO.
SEO Functionality
This is the SEO view when in the platform:

As you can see, when it comes to SEO, Salesforce users aren’t spoilt for choice. If used correctly, these will be the game-changers for your eCommerce SEO.
The URL rules
It’s important to ensure that all URLs for your website are included within the SFCC platform, rather than being created externally as part of customisation (which is more common than you might think!)
Without the correct configuration of URLs, administrators are not able to configure effective URL rules when they are required, resulting in a redundant URL management system.
To configure your SFCC URLs effectively, Salesforce has provided an in depth guide which can be found here.

The URLs - SEO-Friendliness, Catalog URLs, Pipeline URLs and URLs Conflicts
Turn on SEO-Friendly URLs
As overly simplistic as this may sound, SEO-friendly URLs need to be enabled on the platform itself (see below for example). If you launched your site within the last few years, then it is most likely already using this functionality by default. However, if you’ve been on the platform for more than five or so years, you may still be on the older version of URL functionality, so it is important to double check.
A benefit of using the SEO-friendly module is that 301 redirects can be implemented automatically, without needing to manually follow the process. Once the box is ticked, the URLs are refreshed in staging, and all URLs will have 301 redirects from old version to new URLs.
How to Manage Catalog URLs in Salesforce
Location of Catalog URLs: Merchant Tools > SEO > URL Rules > Catalog URLs

Some of the key functions within this category include:
- Locale Mapping – where you can choose for it to be either: sub-folder, hostname or URL parameter
- Character Replacement Settings – the place to decide whether you’re a trailing slash, caps vs no-caps kinda site.
- White-Space – by default SFCC input a “%20” in any areas where there is whitespace in the URL, this can be overridden by specifying that you’d instead prefer a “-” in instances of whitespace. See below:

The rule found (above) will auto replace any sign of & with ‘and’, significantly improve semantic value of your URL structure, and adhere to BERT (Google algorithm update focused on addressing value between words).
Managing Category URL Rules in Salesforce
Moving into Category URL Rules. This section is where SFCC can get complicated, so it’s critical that you keep track of all category IDs (these are all unique).

This (screenshot above) is the section where you can stipulate how your URLs will look once the site goes live.
[ attribute, ID ] – URL would look as follows : /men/smart-shoes
However, you can add more to the URLs than just the end PLP.
[ category-path, [ attribute, ID ] – URL would look as follows : /men/shoes/smart-shoes
Finally, into the Product URL Rules. This is the stage where you’ll need to put your products into their relative category path, category IDs (for SFCC) and their product IDs.
[ category, [ category-path, [ attribute, ID ], / ] ] – URL looks as follows : /men/shoes/smart-shoes/5678.html
Additional setting for category URLs:
- Enable override with page URL 0 allowing you to override the generated URL
- Append trailing slash – categories are considered as directories for the purposes of SEO, and as best practice a directory should be followed by a trailing slash
- Enable category search refinement – category search refinements (filters) allow you to identify specific filters that exist on a page. Rather than those appearing as parameters in the URL, you can make them appear as clean URLs e.g.
/accessories/ties?prefn=refinementColor&prefv1=Red >>>>>>> /ties/red/
Unfortunately, the addition of .html is something that is unchangeable. In order to reduce the potential for duplication, and to reduce the complexity of the site (so that multiple URLs are created for the same product), we recommend that you assign products to the domain, rather than following the relevant category & subcategory path – this way, you’re able to use the same product in multiple different areas around your site. Therefore, a product URL would look as follows:
example-site.co.uk/cotton-training-hoodie/123456.html
Managing Pipeline URLs in Salesforce
Location of URLs: Merchant Tools > SEO > URL Rules > Pipeline URLs
What are pipelines?
- Pipelines are code-based actions that run on Commerce Cloud. For example:
- To display the cart, the action ‘Cart-Show’ runs
- To create a product list page, the action ‘Search-Show’ runs
- You can map pipelines to an ‘alias’ to create a user-friendly URL. Below example has 56 pipelines mapped e.g.:
- Cart-Show to ‘cart’: https://www.example.com/us/cart
- Search-Show to ‘search’: https://www.example.com/us/search?q=badger&lang=en_US
- Your developers can provide a list of pipelines used on your site to identify any that are unmapped – an unmapped pipeline can also be identified from its URL. For example, if Cart-Show was not mapped it would appear as:
- If it was mapped it would appear as:
- https://www.example.com/cart/

Unmapped pipelines will produce undesirable URLs so it is not right from an SEO perspective — we’d begin to see a large influx of unfriendly URLs picked up in the SERP, offering no value to prospecting customers, and impacting the CTR or the site.

The above image shows that aliases have not been localised.
Managing URL Conflicts in Salesforce
Location of URL Conflicts – Merchant Tools > SEO > URL Rules > General
What causes URL conflicts?
- Duplicate attribute values can cause two or more pages to try to generate the same URL.
- Commerce Cloud prevents this by appending version numbers to conflicting URLs
- www.site.com/-1/
- www.site.com/-2/
URL conflicts on category URLs can be seen below.

As the image above shows, 467 conflicting categories are found

From the image above we can see that
Two categories within offers have been given the same value for the customDisplayName used in the URL rule.
Options to correct this:
- If both categories are required: update the attribute in one or both categories to be unique.
- If only one category is required:
- Delete the one no longer required & redirect to the URL with the clean URL (which in this case is without the -1). This will reduce the implication of duplicated content found across your site.
- Or offline the one no longer required and change Category URL Rule setting to not create URLs for offline categories
Recommendation: URL Conflicts should be checked when new categories are created so conflicts can be resolved before replication.
Meta-Data Best Practice
Where is the Meta Data managed in Salesforce Commerce Cloud?
Out-of-the-box functionality: Content in Business Manager takes precedence, if not populated, and uses rules defined in your page templates.
Category:
Merchant Tools > Products and Catalogs > Catalogs > Storefront Catalog > Category > Edit > Category Attributes
Product:
Merchant Tools > Products and Catalogs > Products > Product > General
Folder:
Merchant Tools > Content > Library Folders > Folder > Edit > General
Content:
Merchant Tools > Content > Content Assets > Asset > General
3 Ways to Manage Your Meta-Data in SalesForce Commerce Cloud:
Manually enter information into Business Manager fields for Products, Categories, Folders & Content Assets. Speak to your developers about updating metadata for pipelines/custom pages.
Using the Excel templates provided within SFCC business manager, populate metadata information found on the sheets, run the macro convert which will change it to an XML and upload this into Business Manager
The SEO Meta Tag Rules feature provides merchants the capability to generate and manage meta tag content at scale. It uses rule-based capability to create metadata for home page, product (detail and listing) pages, and content (detail and listing/folder) pages.
Creating Tags Rules in Business Manager
What tags and where?
- Can be used on homepages, products, categories, folders and content assets.
- Can be used for:
- Page titles
- Meta name tags (e.g. description, robots)
- Meta property tags (e.g. OpenGraph)
How?
- Create rules that dynamically insert category/product/content attributes into tag text
- Assign rules to specific categories or the whole catalogue
- Maintain flexibility to override rule with metadata entered in Business Manager (via rule or template code)
- One-time development required to integrate meta tag content into storefront templates (tags can be previewed in Business Manager immediately)
With Meta Tag Rules you have full control to leverage existing static and dynamic content. Here are a couple of examples of rules you could create:
- “Buy $SearchTerm for $RefinementPrice at $SiteName!”
- “IF $RefinementColor (noindex,nofollow) ELSE (index,nofollow)”
- Shop our site for ${Category.displayName} and receive Free Shipping over $100 | ${Site.displayName}
See the SEO Resource Center or speak to your Salesforce representative

If there’s a discrepancy between staging & live (as seen in the image above) then it makes making changes much more difficult — if they’re not matching then how are the titles being generated?
The images below show the way the description is being managed automatically with different Meta Tag rules:
PDP Meta-Tag Rules

PLP Meta-Tag Rules


Image SEO
How to optimise images for search in Salesforce Commerce Cloud
Location: Image Alt & Title – Merchant Tools > Products & Catalogs > Catalogs > Master Catalog > Edit > Image Settings
Alt text (alternative text) is used to describe the appearance and function of an image in machine-readable html code. The primary function of alt text is to be read by screen readers to give visually-impaired users context that would otherwise be derived from viewing the image. It can also provide context to search engines.
A template for generating alt text for product images can be managed within Business Manager:

Bulk uploading PLP copy and H1s is possible, however, the process would need to be discussed with your developers, since there is no OOTB function for this on SFCC.
Crawlability - Sitemaps, Robots.txt and URL Redirects
Sitemaps
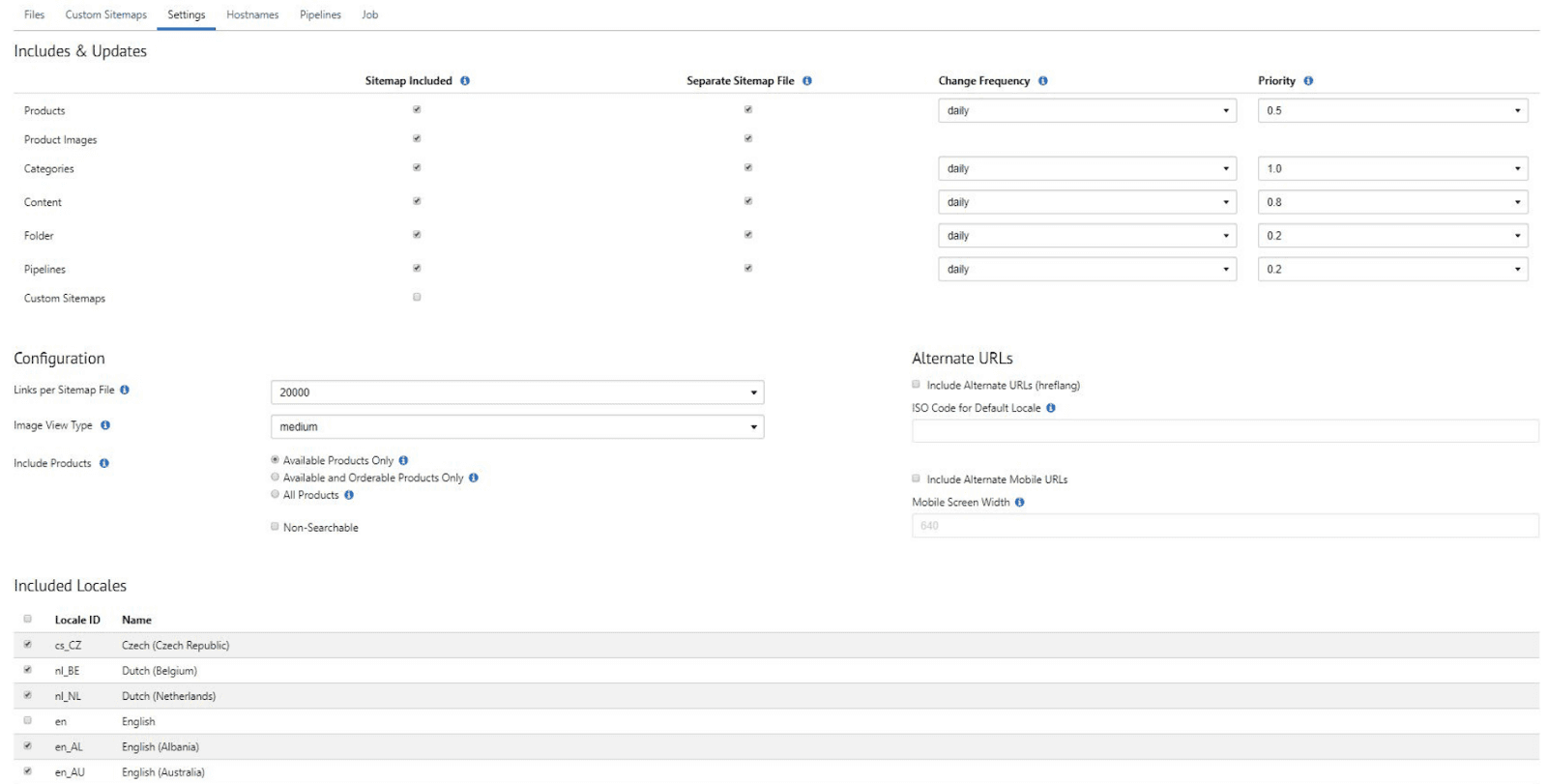
Location of XML Sitemaps: Production > Merchant Tools > SEO > Sitemaps
Historically, search engines found out about pages on a site only by following links to those pages. XML sitemaps can be used to supplement this process, advising search engines that the links within the sitemap files are good-quality pages that should be indexed. The search engine may still decide not to index a page even if it is in the sitemap and may still index pages not in the sitemap that it has found through crawling.

The sitemap is also a critical area for a multisite corporation. The out-of-the-box (OOTB) functionality on SFCC doesn’t allow for large level hreflang tags without the need for complex customisation. Instead, you can utilise the sitemaps for your hreflang requirements, allowing you to connect all of your sites together, targeting specific markets, and reducing the potential for cannibalisation, and improving your global visibility.
To do this you can use the Alternate URLs section as shown in the image below.
Robots.TXT
Location of Robots.txt: Merchant Tools > SEO > Robots > Production
The robots.txt file indicates to search engine robots which pages on the site they should not crawl by using the ‘disallow’ directive.

URL Redirects
Location of URL Redirects: Merchant Tools > SEO > URL Redirects
Create URL redirects when you retire pages or want to create short ‘vanity’ URLs (e.g. for use in print advertising).

Recommendation:
Where possible, source and destinations should be set up as object type (e.g. category, product etc…) and ID rather than URL path. This will help to prevent errors, minimise redirect loops and enable identification of invalid destinations via Advanced Search.
Copy Source Parameters is set to “yes” as default. Managed via Merchant Tools > Site Preferences > Storefront URLs
Finding Invalid URL Redirects
Location: Merchant Tools > SEO > URL Redirects > Advanced > Find Invalid Redirects

When URL redirects are set up with Commerce Cloud objects as destinations, the Find Invalid Redirects function can quickly highlight redirects configured to destinations that no longer exist e.g. EU_SubCategory_10580963 category
Summary
Generally, when we look at the current ecosystem of out-of-the-box CMS platforms such a Shopify, Magento, Woocommerce, etc we see very intuitive, relatively simple platforms that can be easily managed by delegates. However, they come with customisation limitations that are sometimes difficult to overcome.
Salesforce Commerce Cloud’s board scope of customization is the reason that many large companies have opted for Salesforce over smaller CMS platforms. It lets them scale significantly better and in line with the businesses needs and requirements (minus page level hreflang). There are many benefits that we could compare between Salesforce and its smaller competitors, but this is something to be reviewed in a separate article.
The important thing to take away from this guide is the critical setup elements that need to be adhered to in order to set you up for success, especially if you aren’t investing in in-house SEO.
Need more help with managing your Salesforce SEO? We have an award-winning, highly experienced team of technical SEO specialists at hand to offer any further advice. Please feel free to get in touch with us for an informal chat to see if we can help.